Brain tumor surgery in Iran
A brain tumor is a mass caused by the abnormal growth of cells. There are more than 120 types of brain tumors and the most common ones include meningioma and glioma. In general, brain tumors are divided into two groups of primary and secondary tumors based on their origin. Different methods of brain tumor surgery are used to treat these tumors according to the type and location.

Brain tumor surgery in Iran
Surgery is one of the most common treatment methods for all types of brain tumors. The most common types of surgery for brain tumors are:
- sampling (biopsy)
- craniotomy
- Bilateral anterior craniotomy
- “Eyebrow” craniotomy (supraorbital craniotomy)
- “Key slot” craniotomy (retro sigmoid craniotomy)
- Orbit zygomatic craniotomy
- Tran labyrinthine craniotomy
- MRI-guided laser ablation
- Endonasal endoscopy (endonasal endoscopic surgery)
- Neuroendoscopy
Brain tumor treatment continues to progress with new techniques and technologies.
sampling (biopsy)
A biopsy is a surgical procedure to remove a small sample of brain tumor tissue for examination under a microscope. This operation is usually performed at the same time as brain tumor removal surgery (which is called open biopsy). In the following cases, sampling can be done as a separate procedure:
The tumor cannot be removed without damaging important parts of the brain.
The patient is not a candidate for surgery.
After the sample is taken, a pathologist examines the sample to determine the exact type of tumor in terms of malignancy and severity (cancer grading). If doctors can’t take a sample, they determine the diagnosis of a brain tumor and plan the patient’s treatment based on the results of other tests.
craniotomy
Craniotomy is the removal of part of the skull bone for brain surgery. Special tools are used to remove a part of the skull bone, which is called a bone flap. The bone flap is temporarily removed, and then put back in place after Brain tumor surgery in Iran. There are different types of craniotomy.
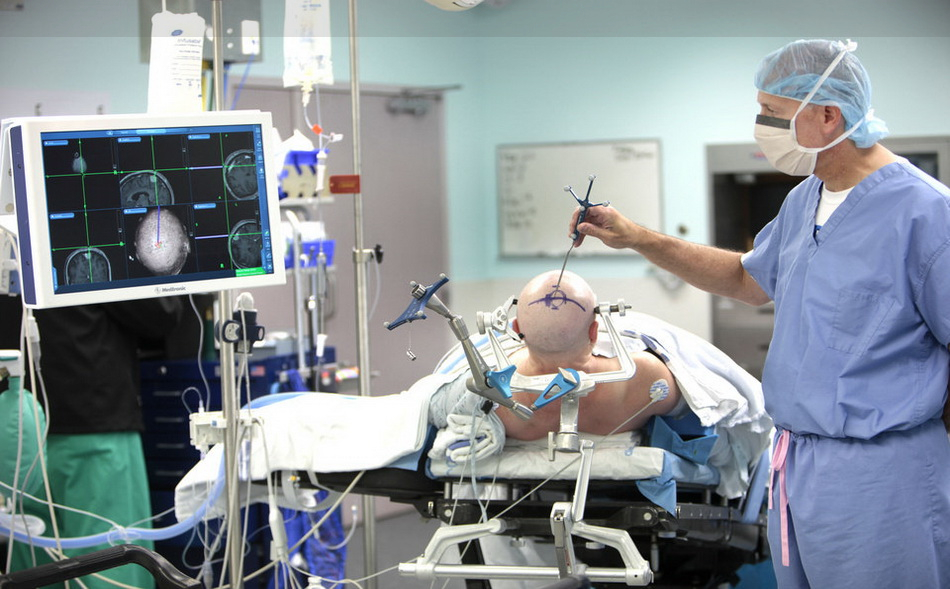
Stereotactic craniotomy
In some craniotomy surgeries, they may use computer guidance with imaging methods (such as MRI or CT) to reach the exact location of the tumor in the brain. This method requires the use of a frame placed on the skull or a frameless system using markers or surface markings on the scalp. When any of these imaging methods are used in conjunction with craniotomy surgery, it is called a stereotactic craniotomy.
From these scans taken from the brain, with the help of a computer, they create a 3D image of the tumor in the brain. This work is useful in distinguishing between tumor tissue and healthy tissue and reaching the exact location of the tumor.
Extended Bifrontal Craniotomy
Bilateral frontal craniotomy is a common procedure in skull surgery used to target tumors on the frontal side of the brain. Based on the principle that cutting the bone of this part is safer than unnecessary manipulation of the brain.
Bilateral craniotomy involves making an incision in the scalp behind the hairline and removing the bone between the eyes and forehead. This bone is put back in place at the end of the surgery. The temporary removal of this bone allows surgeons to work precisely in the space between and behind the eyes without the need for unnecessary manipulation of other parts of the brain.
Bilateral craniotomy is routinely used for those tumors that cannot be removed by minimally invasive approaches due to tumor anatomy, possible tumor pathology, or surgical goals.
Types of candidate tumors for treatment with bilateral brain craniotomy include: meningioma, osteoneuroblastoma, and malignant skull base tumors.
Minimally invasive eyebrow craniotomy
Supra-Orbital craniotomy, which is often called “eyebrow” craniotomy; It is a method used to remove brain tumors. In this method, neurosurgeons make a small incision inside the eyebrow to access tumors in the front of the brain or around the pituitary gland, which is located behind the nose and eyes. When the tumor is very large or close to the optic nerves or vital arteries, this method is used instead of endoscopic endonasal Brain tumor surgery in Iran.
Because it is a minimally invasive procedure, it has advantages. Including :
Less pain than open craniotomy
Faster recovery than open craniotomy
less wound
Supraocular craniotomy may be part of the treatment of Rathke’s cleft cyst, skull base tumors, and some pituitary tumors.
Keyhole Craniotomy (Retro-Sigmoid)
Retro-sigmoid craniotomy, often called “keyhole” craniotomy, is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that provides access to the cerebellum and brainstem through a small incision behind the ear to remove skull base tumors. Neurosurgeons may use this method to reach certain tumors such as meningioma, acoustic neuroma (vestibular schwannoma), skull base tumors, and metastatic brain tumors.
The following are the advantages of this method:
- Less pain after Brain tumor surgery in Iran
- less wound
- Faster recovery
Orbitozygomatic craniotomy
Orbitozygomatic craniotomy is a conventional surgery used to target tumors and aneurysms.
Orbitozygomatic craniotomy, which involves making an incision in the scalp behind the hairline and removing the bone forming the eye-cheek boundary, is typically used for lesions that are too complex to remove with minimally invasive approaches. This bone is repositioned at the end of the surgery.
Brain tumors that may be treated with this method include: craniopharyngioma, pituitary tumors, and meningioma.
Translabyrinthine craniotomy
A translabyrinthine craniotomy is a procedure that involves making an incision in the skin behind the ear, and then removing the mastoid bone and some of the bones of the inner ear (specifically the semicircular canals, which contain receptors for balance). Then the surgeon finds and removes the tumor, or tries to reduce the severity of the tumor as much as possible.
When the patient has no or useful hearing, the translabyrinthine method is often considered to remove acoustic neuromas. During this procedure, the semicircular canals of the ear are removed to access the tumor. As a result, complete hearing loss occurs.
Although hearing is lost with translabyrinthine craniotomy, the risk of facial nerve damage may be reduced.
Endoscopic endonasal surgery
Endonasal endoscopic Brain tumor surgery in Iranis a minimally invasive technique that allows the surgeon to go through the nose to operate on the front of the brain and upper spine.
A thin tube called an endoscope is passed through the nose and sinuses. This allows your surgeon to access parts of the brain that are difficult to reach using traditional surgical approaches, often requiring large incisions and removing parts of the skull.
This method can be used to remove tumors in areas near the base of the brain or skull and above the spine. It can also be used to treat sinus problems. This method allows the surgeon to reach these areas without having to make large incisions or remove parts of the skull. And it often results in a faster and less painful recovery.
Neuroendoscopy
Neuroendoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure in which the neurosurgeon removes the tumor through small holes in the skull or through the mouth or nose.
Neuroendoscopy enables neurosurgeons to:
to access areas of the brain that cannot be accessed by traditional surgery.
Remove the tumor without cutting or damaging other parts of the skull.
Neuroendoscopy uses an endoscope, a small telescope-like device, equipped with a high-definition video camera and a monocular at the end; So that the neurosurgeon can direct the device to the tumor and gain access to it. To remove a tumor or take a sample from it (sampling), neurosurgeons attach a special instrument (often an additional endoscope with forceps and a cutter at the end) to the endoscope.
Brain tumors that may be treated with neuroendoscopy include:
- Tumors of the pineal region
- Pituitary tumors
- Rathke’s cleft cyst
- Skull base tumors
- Ventricular tumors
MRI-guided laser ablation
MRI-guided laser ablation is a minimally invasive neurosurgical procedure for a number of diseases, including brain tumors. In this treatment, a laser is used to target and destroy the tumor. This method can help surgeons reach and treat the most serious brain tumors, including glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) and brain tumors located close to sensitive brain structures that are difficult to access through traditional open surgery (craniotomy). , help.
The advantages of this method include reducing pain after surgery and shortening the recovery time compared to craniotomy.
Brain surgery with consciousness
Conscious brain surgery was primarily used to treat epileptic seizures and Parkinson’s disease, but is increasingly being used to remove brain tumors located in areas that can affect important functions. Consciousness allows you to answer questions that help the surgeon identify areas of the brain that affect functions such as vision, movement, or speech. The surgeon uses this information to precisely target treatment.
In conscious brain surgery, the patient still receives sedation and pain relief from their anesthesiologist. He controls the blood pressure, heart rate and oxygen of the patient and is always by his side. Additionally, the surgeon may use local anesthesia to numb the scalp.
Of course, the patient will not necessarily be fully aware at all stages of the work. The anesthesiologist can adjust the level of drugs during surgery to wake up the person only when necessary. Even then, the patient may not need to be fully conscious to speak. Instead, the patient may be placed in a position where he can respond by squeezing the hand or giving another signal. Some patients don’t even remember being awake.
Preoperative discussions with the anesthesiologist can help people reduce any anxiety about this type of surgery.
Brain tumor surgery in Iran
الدکتور مهدي زينلی الزادة – استاذ جراحة المخ و قاعدة الجمجمة
Endoscopic Pituitary Surgery in Iran